The Australian government has been running a trial of ISP-level filtering products to determine whether network-based filtering could be implemented by the government to censor certain forms of online content without a major degradation of overall network performance. The government’s report on the issue was released today: Closed-Environment Testing of ISP-Level Internet Content Filtering. It was produced by the Australian Communications & Media Authority (ACMA), which is the rough equivalent of the Federal Communications Commission here in the U.S., but with somewhat broader authority.
The Australian government has been investigating Internet filtering techniques for many years now and even gone so far to offered subsidized, government-approved PC-based filters through the Protecting Australian Families Online program. That experiment did not end well, however, as a 16-year old Australian youth cracked the filter within a half hour of its release. The Australian government next turned its attention to ISP-level filtering as a possible solution and began a test of 6 different network-based filters in Tasmania.
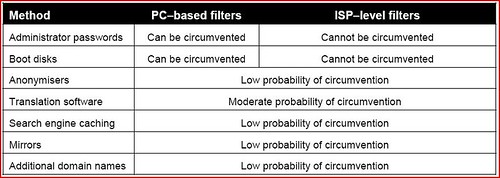
What makes ISP-level (network-based) filtering an attractive approach for many policymakers is that, at least in theory, it could solve the problem the Australian government faced with PC-based (client-side) filters: ISP-level filters are more difficult, if not impossible, to circumvent. That is, if you can somehow filter content and communications at the source–or within the network–then you have a much greater probability of stopping that content from getting through. Here’s a chart from the ACMA’s new report that illustrates what they see as the advantage of ISP-level filters:

 The Technology Liberation Front is the tech policy blog dedicated to keeping politicians' hands off the 'net and everything else related to technology.
The Technology Liberation Front is the tech policy blog dedicated to keeping politicians' hands off the 'net and everything else related to technology.