Chairman Thomas E. Wheeler of the Federal Communications Commission unveiled his proposal this week for regulating broadband Internet access under a 1934 law. Since there are three Democrats and two Republicans on the FCC, Wheeler’s proposal is likely to pass on a party-line vote and is almost certain to be appealed.
Free market advocates have pointed out that FCC regulation is not only unnecessary for continued Internet openness, but it could lead to years of disruptive litigation and jeopardize investment and innovation in the network.
Writing in WIRED magazine, Wheeler argues that the Internet wouldn’t even exist if the FCC hadn’t mandated open access for telephone network equipment in the 1960s, and that his mid-1980s startup either failed or was doomed because the phone network was open whereas the cable networks (on which his startup depended) were closed. He also predicts that regulation can be accomplished while encouraging investment in broadband networks, because there will be “no rate regulation, no tariffs, no last-mile unbundling.” There are a number of problems with Chairman Wheeler’s analysis. First, let’s examine the historical assumptions that underlie the Wheeler proposal.
Continue reading →
Farhad Manjoo’s latest New York Times column, “Giving the Drone Industry the Leeway to Innovate,” discusses how the Federal Aviation Administration’s (FAA) current regulatory morass continues to thwart many potentially beneficial drone innovations. I particularly appreciated this point:
But perhaps the most interesting applications for drones are the ones we can’t predict. Imposing broad limitations on drone use now would be squashing a promising new area of innovation just as it’s getting started, and before we’ve seen many of the potential uses. “In the 1980s, the Internet was good for some specific military applications, but some of the most important things haven’t really come about until the last decade,” said Michael Perry, a spokesman for DJI [maker of Phantom drones]. . . . He added, “Opening the technology to more people allows for the kind of innovation that nobody can predict.”
That is exactly right and it reflects the general notion of “permissionless innovation” that I have written about extensively here in recent years. As I summarized in a recent essay: “Permissionless innovation refers to the notion that experimentation with new technologies and business models should generally be permitted by default. Unless a compelling case can be made that a new invention or business model will bring serious harm to individuals, innovation should be allowed to continue unabated and problems, if they develop at all, can be addressed later.” Continue reading →
This month, the FCC is set to issue an order that will reclassify broadband under Title II of the Communications Act. As a result of this reclassification, broadband will suddenly become subject to numerous federal and local taxes and fees.
How much will these new taxes reduce broadband subscribership? Nobody knows for sure, but using the existing economic literature we can come up with a back-of-the-envelope calculation.
According to a policy brief by Brookings’s Bob Litan and the Progressive Policy Institute’s Hal Singer, reclassification under Title II will increase fixed broadband costs on average by $67 per year due to both federal and local taxes. With pre-Title II costs of broadband at $537 per year, this represents a 12.4 percent increase.
[I have updated these estimates at the end of this post.]
Continue reading →
After some ten years, gallons of ink and thousands of megabytes of bandwidth, the debate over network neutrality is reaching a climactic moment.
Bills are expected to be introduced in both the Senate and House this week that would allow the Federal Communications Commission to regulate paid prioritization, the stated goal of network neutrality advocates from the start. Led by Sen. John Thune (R-S.D.) and Rep. Fred Upton (R-Mich.), the legislation represents a major compromise on the part of congressional Republicans, who until now have held fast against any additional Internet regulation. Their willingness to soften on paid prioritization has gotten the attention of a number of leading Democrats, including Sens. Bill Nelson (D-Fla.) and Cory Booker (D-N.J.). The only question that remains is if FCC Chairman Thomas Wheeler and President Barack Obama are willing to buy into this emerging spirit of partisanship.
Obama wants a more radical course—outright reclassification of Internet services under Title II of the Communications Act, a policy Wheeler appears to have embraced in spite of reservations he expressed last year. Title II, however, would give the FCC the same type of sweeping regulatory authority over the Internet as it does monopoly phone service—a situation that stands to create a “Mother, may I” regime over what, to date, has been an wildly successful environment of permissionless innovation.
Continue reading →
My employer, the Mercatus Center, provides ridiculously generous funding (up to $40,000/year) for graduate students. There are several opportunities depending on your goals, but I encourage people interested in technology policy to particularly consider the MA Fellowship, as that can come with an opportunity to work with the tech policy team here at Mercatus. Mind the deadlines!
The PhD Fellowship is a three-year, competitive, full-time fellowship program for students who are pursuing a doctoral degree in economics at George Mason University. Our PhD Fellows take courses in market process economics, public choice, and institutional analysis and work on projects that use these lenses to understand global prosperity and the dynamics of social change. Successful PhD Fellows have secured tenure track positions at colleges and universities throughout the US and Europe.
It includes full tuition support, a stipend, and experience as a research assistant working closely with Mercatus-affiliated Mason faculty. It is a total award of up to $120,000 over three years. Acceptance into the fellowship program is dependent on acceptance into the PhD program in economics at George Mason University. The deadline for applications is February 1, 2015.
Continue reading →
Last month, my Mercatus Center colleague Brent Skorup published a major scoop: police departments around the country are scanning social media to assign people individualized “threat ratings” — green, yellow, or red. This week, police are complaining that the public is using social media to track them back.
LAPD Chief Charlie Beck has expressed concerns that Waze, the social traffic app owned by Google, could be used to target police officers. The National Sherriff’s Association has also complained about the app.
To be clear, Waze does not allow anybody to track individual officers. Users of the app can drop a pin on a map letting drivers know that there is police activity (or traffic jams, accidents, or traffic enforment cameras) in the area.
That’s it.
Continue reading →
I suppose it was inevitable that the DRM wars would come to the world of drones. Reporting for the Wall Street Journal today, Jack Nicas notes that:
In response to the drone crash at the White House this week, the Chinese maker of the device that crashed said it is updating its drones to disable them from flying over much of Washington, D.C.SZ DJI Technology Co. of Shenzhen, China, plans to send a firmware update in the next week that, if downloaded, would prevent DJI drones from taking off within the restricted flight zone that covers much of the U.S. capital, company spokesman Michael Perry said.
Washington Post reporter Brian Fung explains what this means technologically:
The [DJI firmware] update will add a list of GPS coordinates to the drone’s computer telling it where it can and can’t go. Here’s how that system works generally: When a drone comes within five miles of an airport, Perry explained, an altitude restriction gets applied to the drone so that it doesn’t interfere with manned aircraft. Within 1.5 miles, the drone will be automatically grounded and won’t be able to fly at all, requiring the user to either pull away from the no-fly zone or personally retrieve the device from where it landed. The concept of triggering certain actions when reaching a specific geographic area is called “geofencing,” and it’s a common technology in smartphones. Since 2011, iPhone owners have been able to create reminders that alert them when they arrive at specific locations, such as the office.
This is complete overkill and it almost certainly will not work in practice. First, this is just DRM for drones, and just as DRM has failed in most other cases, it will fail here as well. If you sell somebody a drone that doesn’t work within a 15-mile radius of a major metropolitan area, they’ll be online minutes later looking for a hack to get it working properly. And you better believe they will find one. Continue reading →
Yesterday, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) released its long-awaited report on “The Internet of Things: Privacy and Security in a Connected World.” The 55-page report is the result of a lengthy staff exploration of the issue, which kicked off with an FTC workshop on the issue that was held on November 19, 2013.
I’m still digesting all the details in the report, but I thought I’d offer a few quick thoughts on some of the major findings and recommendations from it. As I’ve noted here before, I’ve made the Internet of Things my top priority over the past year and have penned several essays about it here, as well as in a big new white paper (“The Internet of Things and Wearable Technology: Addressing Privacy and Security Concerns without Derailing Innovation”) that will be published in the Richmond Journal of Law & Technology shortly. (Also, here’s a compendium of most of what I’ve done on the issue thus far.)
I’ll begin with a few general thoughts on the FTC’s report and its overall approach to the Internet of Things and then discuss a few specific issues that I believe deserve attention. Continue reading →
Congress is considering reforming television laws and solicited comment from the public last month. On Friday, I submitted a letter encouraging the reform effort. I attached the paper Adam and I wrote last year about the current state of video regulations and the need for eliminating the complex rules for television providers.
As I say in the letter, excerpted below, pay TV (cable, satellite, and telco-provided) is quite competitive, as this chart of pay TV market share illustrates. In addition to pay TV there is broadcast, Netflix, Sling, and other providers. Consumers have many choices and the old industrial policy for mass media encourages rent-seeking and prevents markets from evolving.
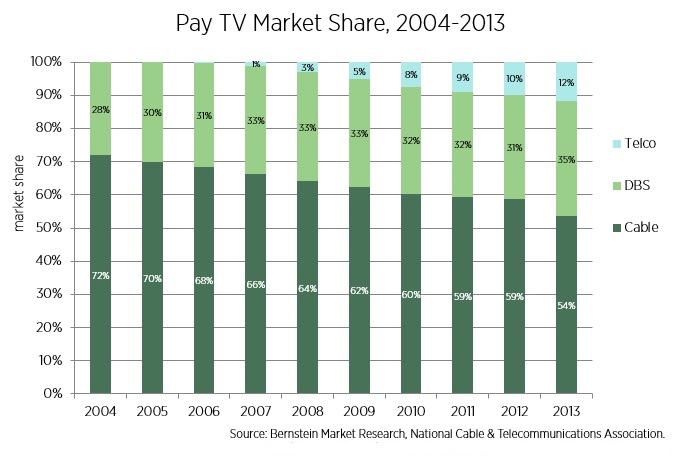
Continue reading →

Originally posted at Medium.
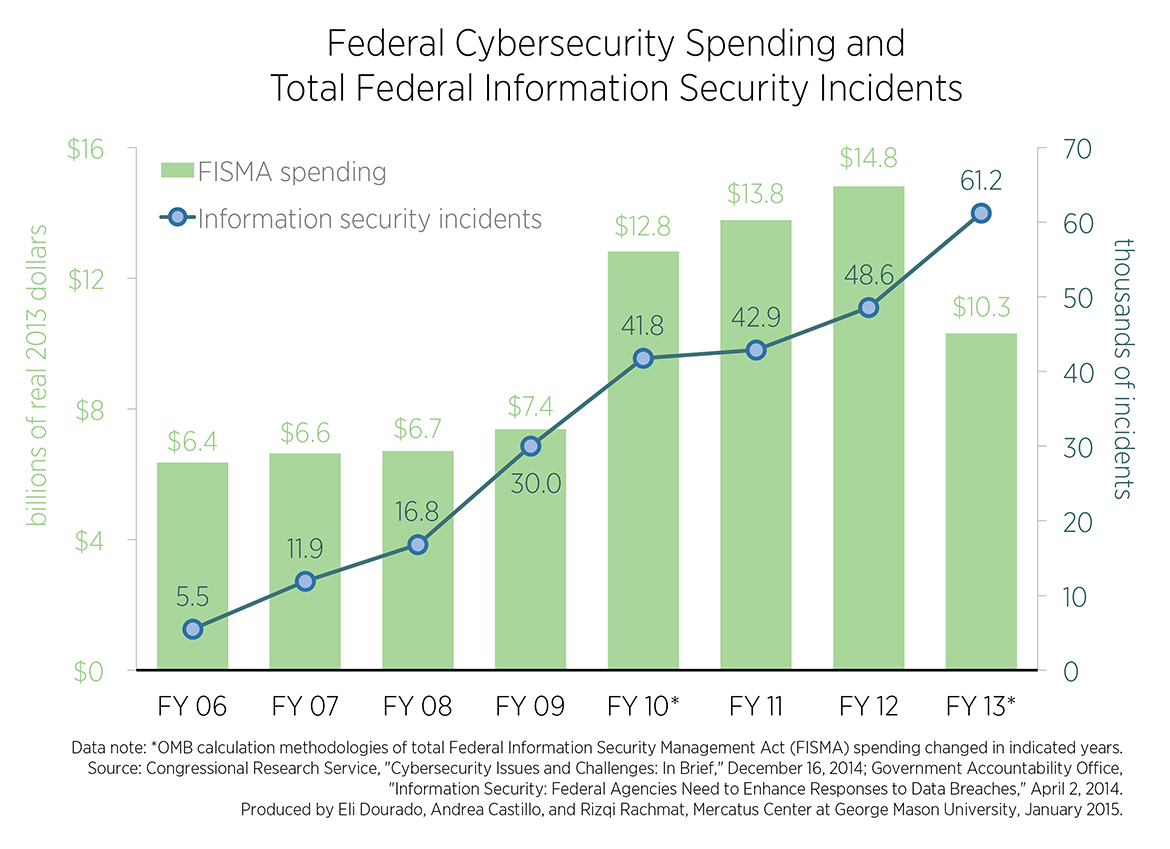
The federal government is not about to allow last year’s rash of high-profile security failures of private systems like Home Depot, JP Morgan, and Sony Entertainment to go to waste without expanding its influence over digital activities.



 The Technology Liberation Front is the tech policy blog dedicated to keeping politicians' hands off the 'net and everything else related to technology.
The Technology Liberation Front is the tech policy blog dedicated to keeping politicians' hands off the 'net and everything else related to technology.