I can’t help but think that there might be a big advantage of having the AT&T-T-Mobile merger go to court. For once, the high-profile action everyone pays attention to will occur in an antitrust forum where the decision criterion is the effects of the merger on consumer welfare, period. Regardless of what one thinks about the merger, it’s nice to see that we’ll finally have a knock-down, drag-out fight based on whether a big telecommunications merger harms consumers and competition. That’s the antitrust standard the Department of Justice has to satisfy in order to prevent the merger.
This will be a refreshing change from the Federal Communications Commission’s “public interest” standard, which allows the commission to object on grounds other than consumer welfare and demand all manner of concessions that have nothing to do with remedying anticompetitive effects of a deal. Case in point: Comcast must now offer broadband service for $9.95 per month to low-income households as a condition for getting approval to buy 51 percent of NBCUniversal. Now, I’m all for seeing low-income households get access to broadband, but subsidizing one subset of customers has little to do with mitigating any possible anticompetitive effects of allowing a cable company to own NBCUniversal. As FCC Commissioners McDowell and Baker said in their statement on that transaction, “Any proposed remedies should be narrow and transaction specific, tailored to address particular anti-competitive harms. License transfer approvals should not serve as vehicles to extract from petitioners far-reaching and non-merger specific policy concessions that are best left to broader rulemaking or legislative processes.”
In short, if AT&T wins in court, the FCC should approve the merger promptly without additional conditions.

 In an
In an 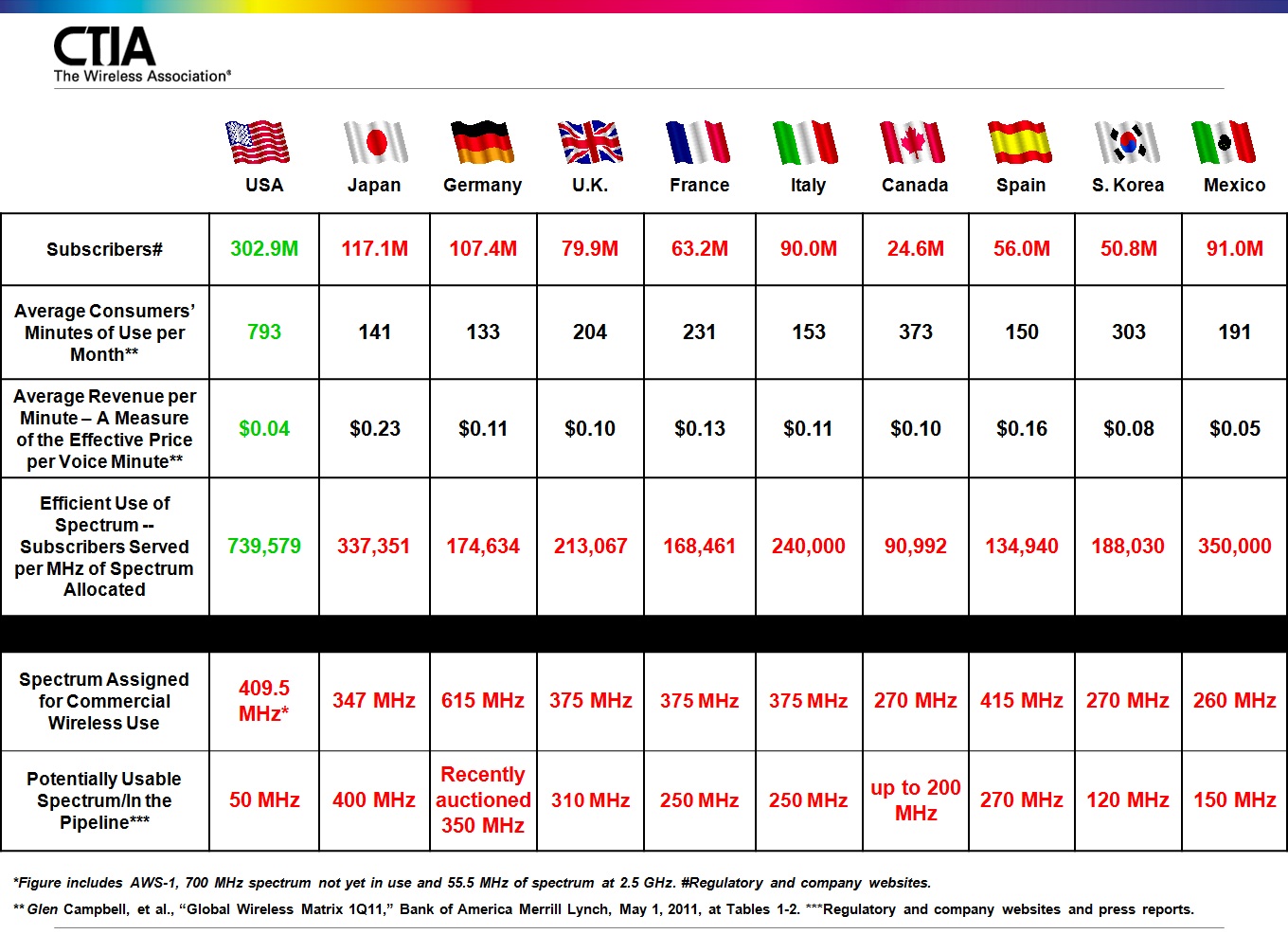

 The Technology Liberation Front is the tech policy blog dedicated to keeping politicians' hands off the 'net and everything else related to technology.
The Technology Liberation Front is the tech policy blog dedicated to keeping politicians' hands off the 'net and everything else related to technology.